Car steering systems are crucial components that enable drivers to control the direction of their cars with the help of different types of gearbox. In this guide, we will explore different types of car steering, including rack and pinion, recirculating ball, and electric power steering (EPS). For each type, we will delve into their advantages, disadvantages, working principles, responsiveness, and maintenance requirements, offering insights to help car owners understand and choose the most suitable steering system for their cars.
What is Car Steering?
Car steering refers to the mechanism by which a driver controls the direction of a car’s movement. Typically located in front of the driver, the steering system allows for precise manoeuvring by turning the wheels in response to input from the driver. Modern cars commonly use a rack and pinion steering system, where the rotational motion of the steering wheel is translated into linear motion to turn the wheels. Other types of steering systems include recirculating ball steering and electronically assisted steering. Regardless of the specific mechanism, the primary function of car steering is to enable the driver to navigate safely and efficiently, providing control over the car’s trajectory on the road.
Types of Car Steering
Car steering is the system that allows you to control the direction of your car by turning the front wheels. It’s essentially a network of connected parts that translates the rotation of the steering wheel in your hands to the left and right movement of the front wheels. Different types of car steering along with description are given below.
|
Type of Car Steering |
Description |
| Rack and Pinion Steering | Utilises a rack and pinion mechanism to translate steering wheel input into linear motion, turning the wheels for directional control. |
| Recirculating Ball Steering | Features a threaded rod with recirculating ball bearings to transmit steering input, commonly found in older vehicles and heavy-duty trucks. |
| Electric Power Steering (EPS) | Uses an electric motor to assist with steering, offering variable assistance based on driving conditions and vehicle speed. |
| Hydraulic Power Steering | Relies on hydraulic pressure generated by a pump to assist with steering effort, commonly found in older vehicles and some modern trucks. |
| Direct Adaptive Steering | Employs electronic actuators to control steering inputs directly, without mechanical linkage, providing precise control and customizable steering feel. |
Car Steering: A Breakdown by Type
The car steering system in the car is the process of running the car in the desired direction by turning, usually the front wheels and for effective control of the car throughout its speed range with safety, proper steering is necessary. The system allows a driver to use only light forces to steer a heavy car. Different types of car steering with their advantages are given below.
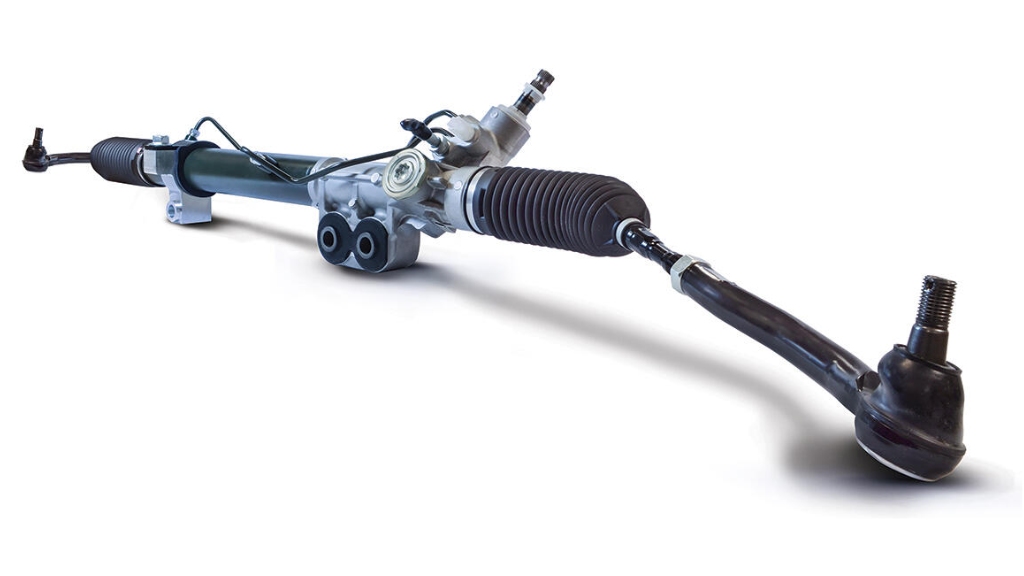
1. Rack and Pinion Steering
Rack and pinion steering utilises a rack and pinion mechanism to translate steering wheel input into linear motion, turning the wheels for directional control.

-
Advantages:
- Provides precise and responsive steering, offering good feedback to the driver.
- Compact and lightweight design, suitable for a wide range of cars.
2. Recirculating Ball Steering
Recirculating ball steering features a threaded rod with recirculating ball bearings to transmit steering input, commonly found in older vehicles and heavy-duty trucks.
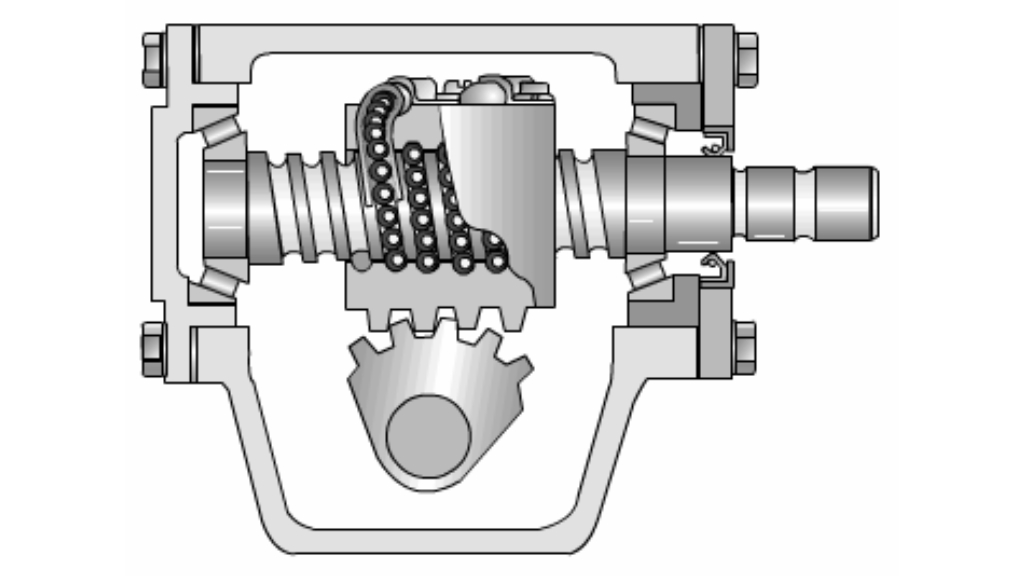
-
Advantages:
- Offers smoother operation and reduced steering effort compared to manual steering systems.
- Provides durability and reliability, suitable for rugged applications and heavy cars.
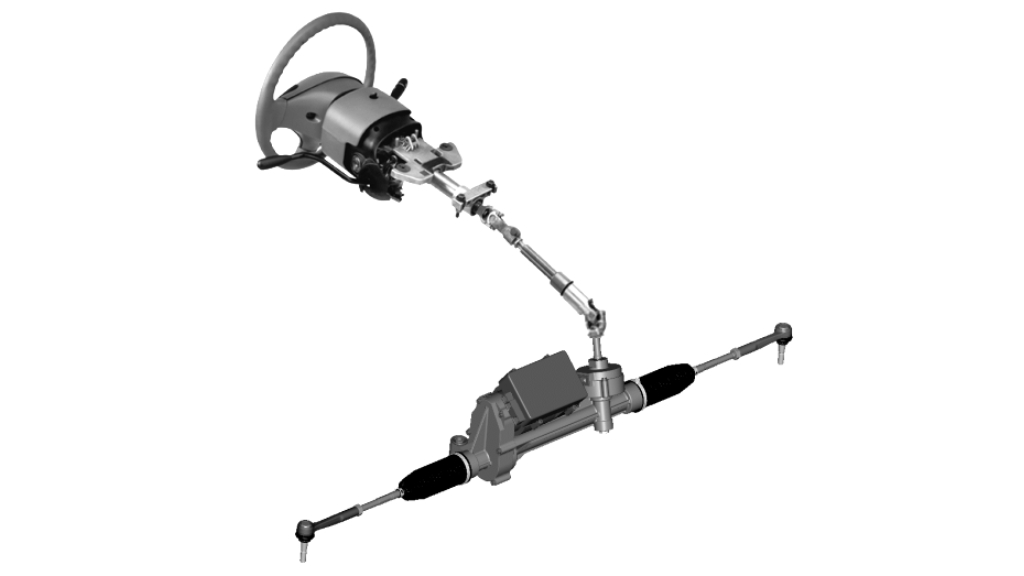
3. Electric Power Steering (EPS)
Electric power steering uses an electric motor to assist with steering, offering variable assistance based on driving conditions and vehicle speed.

-
Advantages:
- Provides precise and effortless steering, with adjustable assistance levels for different driving situations.
- Improves fuel efficiency by reducing parasitic losses compared to hydraulic power steering.
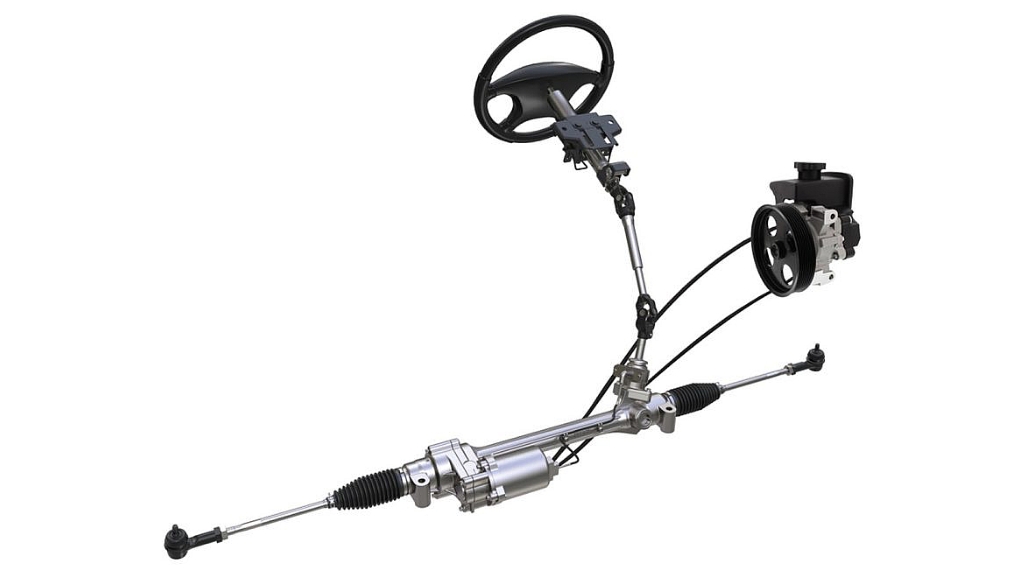
4. Hydraulic Power Steering
Hydraulic power steering relies on hydraulic pressure generated by a pump to assist with steering effort, commonly found in older vehicles and some modern trucks.

-
Advantages:
- Offers smooth and consistent steering assistance across a wide range of driving conditions.
- Provides good road feel and feedback to the driver, enhancing control and confidence.
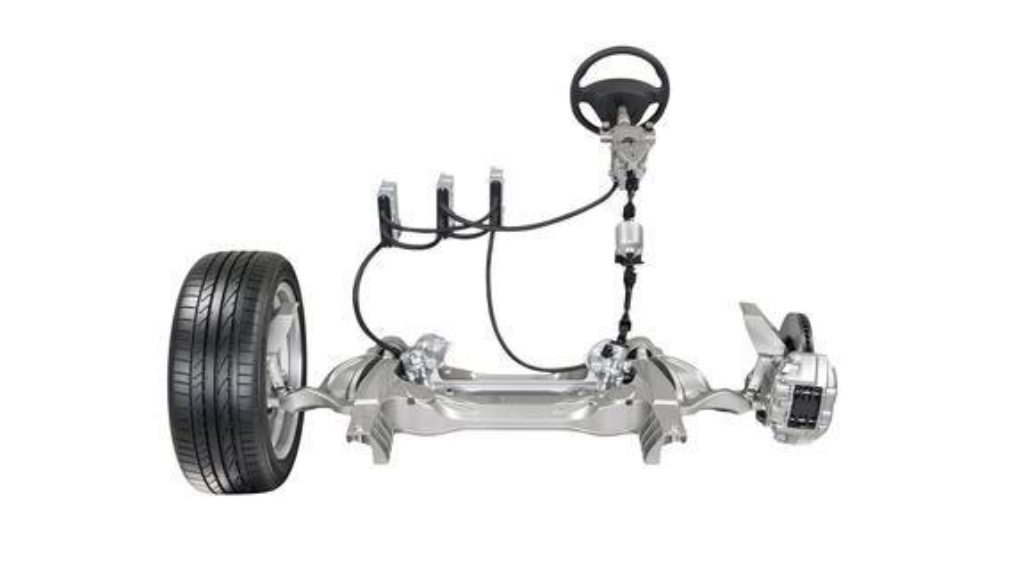
5. Direct Adaptive Steering
Direct adaptive steering employs electronic actuators to control steering inputs directly, without mechanical linkage, providing precise control and a customizable steering feel.

-
Advantages:
- Offers customizable steering characteristics, allowing drivers to adjust steering effort and response to their preferences.
- Provides enhanced precision and feedback compared to traditional steering systems.
Conclusion
There isn’t a single best car steering system that applies universally. The ideal system depends on several factors, including:
Car Type:
- Performance cars: Often benefit from a more direct steering feel offered by hydraulic rack and pinion systems for precise handling.
- Larger vehicles (SUVs): Might prioritise comfort and ease of manoeuvring, making electric power steering (EPS) with its lighter steering feel a good option.
Driver Preference:
- Some drivers enjoy a more connected and responsive steering feel which might favour hydraulic systems.
- Others prefer a lighter touch and easier manoeuvring and EPS could be a better fit.






Leave a Reply